Exploring the Secret Door of Signal Amplification
In daily life, signal amplification can be seen everywhere. For example, after the audio system processes the tiny audio signal, it drives the speaker to produce a loud and clear sound; in the field of communications, the weak signal of the mobile phone is enhanced by the base station power amplifier to achieve long-distance stable communication. All of these are inseparable from the power amplifier. So, what signal does the power amplifier amplify? How does it work? Next, let's explore the world of power amplifiers and unveil the veil of signal amplification.
Exploring the Basics of Power Amplifiers
(I) What is a power amplifier?
The power amplifier in English is "power amplifier", or "power amplifier" for short. It is an electronic amplifier that can generate maximum power output to drive the load (such as speakers, motors, antennas, etc.) at a given distortion rate. It plays a key role in electronic systems, and its performance affects the system signal output. For example, in the audio system, it receives the low-power audio signal output by the sound source device and amplifies it to provide enough power for the speaker so that we can hear clear and loud sound. In essence, its task is to increase the input signal power and drive the load to work normally.
(II) Basic working principle
The basic working principle of the power amplifier is to use devices such as transistors or field effect transistors. Taking transistors as an example, the current control function of transistors is used to convert the power supply power into a current that changes with the input signal. The collector current of the transistor is β times the base current. A small signal is injected into the base to amplify the signal current. A large signal is obtained through isolation by a DC blocking capacitor, and the power amplification is completed by continuous amplification.
In the actual power amplifier circuit, the input signal is first amplified and adjusted by the preamplifier, and then enters the power amplifier part. The device converts the power distribution of the power supply according to the input signal, amplifies the signal power to the required output power level, and finally outputs it to the load to drive it to work. The whole process often uses negative feedback technology, feeds back part of the output signal to the input end for comparison with the input signal, uses the difference signal to control the amplifier circuit, adjusts the gain and stability, ensures that the output signal waveform is consistent with the input, and reduces distortion.
The type of signal being amplified is revealed
(I) Audio signal: playing the magnificent chapter of sound
Audio signal is a common signal type for power amplifiers. It is converted from sound waves into analog electrical signals by sensors. Its frequency range is from 20Hz to 20kHz, covering the frequency that can be perceived by the human ear. Power amplifiers play a key role in the audio field. In the audio system, they receive and amplify the low-power audio signals output by the audio source device, power the speakers, and make them produce clear and loud sounds. For example, in home theaters, large concerts, radio stations and other scenes, power amplifiers are needed to amplify audio signals to meet different playback requirements.
(II) RF signals: the bridge of wireless communication
RF signals are the key signal type for wireless data transmission in the field of wireless communication. Radio frequency (RF) refers to the frequency range of 300kHz - 300GHz. Signals in this frequency band can be radiated into space through antennas to achieve wireless communication.
In wireless communication systems, from mobile devices to base stations and satellite communications, RF power amplifiers are indispensable for amplifying RF signals. Taking mobile phone communications as an example, the RF power amplifier in the mobile phone amplifies the weak RF signal processed by the baseband chip, and establishes a communication connection with the base station through antenna transmission to realize functions such as calls, text messages, and Internet access. The base station needs to amplify and forward the mobile phone signal. In satellite communications, the RF power amplifier on the satellite realizes signal amplification and forwarding to complete global communication coverage. The performance of RF power amplifiers affects the transmission distance, signal quality and communication capacity of wireless communication systems. In the 5G era, there are higher requirements for its linearity, efficiency and bandwidth.
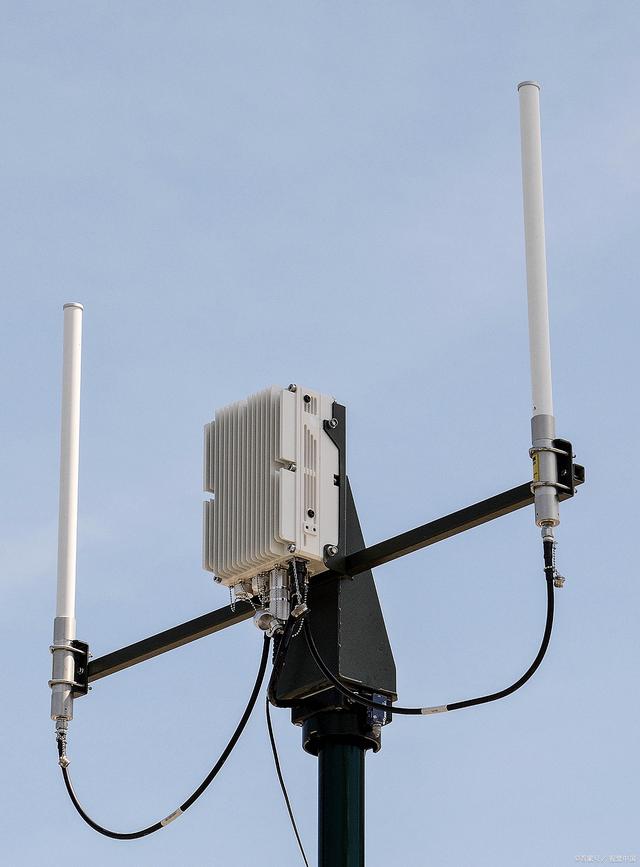

(III) Sensor signals: a boost to the perception of the world
In modern industrial production, environmental monitoring, medical equipment and other fields, various sensors play an important role and can convert physical quantities such as temperature and pressure into analog electrical signals. However, the original signal is weak and difficult to be recognized and used by subsequent circuits or systems, so a power amplifier is needed to amplify it.
For example, temperature sensors, in industrial production, convert temperature changes into weak electrical signals, which are amplified by power amplifiers and transmitted to temperature control systems to achieve precise temperature control; pressure sensors in the automotive, aerospace and other fields convert pressure signals into electrical signals and then amplify them through power amplifiers to provide a basis for data analysis; sensors in medical equipment convert human bioelectrical signals into weak electrical signals, which are amplified for doctors to diagnose health conditions.
Different types of power amplifiers and signal amplification
(I) Class A power amplifier: a defender of sound quality
Class A power amplifiers, also known as Class A power amplifiers, are amplifiers in a completely linear amplification form. When working, the positive and negative channels of the transistor are always open regardless of whether there is a signal or not. Even without an input signal, it consumes power and generates heat. It has high linearity, and the output and input signal waveforms and phases are the same, with almost no distortion. It can accurately restore signal details and dynamic range, such as in high-end audiophile audio systems. However, it has low efficiency, only 20% - 30%, and high energy consumption. It is mostly suitable for occasions with extremely high requirements for sound quality and insensitive to efficiency and cost, such as high-end audio equipment, professional recording studios, etc.
(II) Class B power amplifier: the pursuer of efficiency
Class B power amplifier adopts a push-pull design, which is different from the principle of Class A power amplifier. When working, the positive and negative channels of the transistor are always closed, and they are turned on only when there is a signal input. When the positive phase signal comes, the positive phase channel works and the negative phase channel is closed. The two channels do not work at the same time, and there is no power loss in the signal-free part. The efficiency can reach about 70%. However, the Class B amplifier has the problem of crossover distortion. When the input signal switches between the positive and negative half cycles, the transistor has a conduction voltage. When the signal is close to zero level, the two transistors are cut off, and the output signal is distorted, which is more obvious at low levels. This makes it unsuitable for occasions with high requirements for sound quality. However, it still has room for application in signal amplification scenarios that do not require high distortion and pursue high efficiency, such as early car audio and industrial control signal amplification.
(III) Class AB power amplifier: the art of balance
The Class AB power amplifier combines the advantages of Class A and Class B to find a balance between efficiency and distortion. When there is no signal or the signal is weak, the positive and negative channels of the transistor are weakly turned on, and the power loss is small; when the signal becomes stronger, the working mode is similar to that of the Class B amplifier, and the positive and negative half-cycle signals are amplified in different channels, which not only reduces the power loss of the Class A amplifier, but also reduces the crossover distortion of the Class B amplifier. It is widely used in the audio field, such as car audio, home theater system, KTV audio, etc. In car audio, it can power speakers and ensure sound quality under limited conditions; in home theater systems, it can drive multi-channel speakers to create surround sound effects.
(IV) Class D power amplifier: the new favorite in the digital age
Class D power amplifier uses digital pulse modulation technology, also known as digital power amplifier, and its working principle is different from that of traditional analog power amplifiers. It first samples and quantizes the input signal into a digital signal, and then converts it into a high-frequency pulse signal through technologies such as PWM or PDM. The power converter drives the switching transistor to convert the pulse signal into an analog signal output. Because the switching transistor has only two states, "on" and "off", the energy loss is small, the efficiency exceeds 90%, and it is small in size, light in weight, and low in distortion. It is widely used in portable devices (such as mobile phones, tablets, Bluetooth speakers, etc.) that have strict requirements on power consumption and volume, and it is also emerging in high-performance audio systems.
Practical application case analysis
(I) Home audio system: immersive music experience
Imagine a weekend night, you are curled up on the sofa ready to watch a movie, press the remote control to start the home theater system, and the power amplifier starts working. It is like a conductor, receiving low-power audio signals output by devices such as Blu-ray players, which cannot directly drive the speakers.

Taking a 5.1-channel home theater system as an example, the power amplifier divides the audio signal into six channel signals, and amplifies the power of each channel signal several times or even dozens of times through the internal amplification circuit, so that the speakers can vividly restore the movie sound effects and bring a shocking experience.
In the Hi-Fi audio system, the power amplifier has extremely high requirements for sound quality restoration and pursues high-fidelity playback. High-end Hi-Fi power amplifiers use Class A or Class AB amplification technology and high-quality components to clearly present music details, whether it is classical or rock, it can immerse music lovers.
(II) Mobile communication: unimpeded connection
In the digital age, mobile phones are an indispensable part of life, and their functions are inseparable from power amplifiers. When a mobile phone makes a call or sends a message, the baseband chip converts the voice and data signals into radio frequency signals, but the signal power is weak and will decay rapidly when directly transmitted, and it cannot communicate with the base station. At this time, the power amplifier amplifies the weak RF signal to a level that can overcome the transmission loss. The output power can generally reach several hundred milliwatts or even several watts. The amplified signal can establish a stable communication link with the base station.
In actual communication, the power amplifier will dynamically adjust the output power according to the distance between the mobile phone and the base station, the signal strength, etc., reduce the power when close to the base station, and increase the power in the weak signal area. This mechanism ensures stable and reliable communication and extends battery life. With the development of 5G, higher performance requirements are placed on power amplifiers, which need to have a wider bandwidth, higher linearity and efficiency. To this end, mobile phone manufacturers and chip manufacturers continue to develop new technologies, such as using new materials such as gallium nitride to improve performance and efficiency.
(III) Industrial automation production line: guarantee of precise control
In modern industrial production, industrial automation production lines are the key to improving production efficiency and ensuring product quality. Power amplifiers are an important part of signal processing and control and play an indispensable role.
In the automated production line of an automobile manufacturing plant, various sensors are responsible for monitoring physical quantities and converting them into electrical signals, but these signals are weak and susceptible to interference and cannot be directly processed by the control system. The power amplifier amplifies, filters, and shapes them into standard signals. For example, in the welding process of automobile bodies, the position sensor signal is amplified by the power amplifier and transmitted to the control system to ensure the precise operation of the welding robot and guarantee the welding quality; if there is no power amplifier, the product quality will be affected.
In addition, the power amplifier also drives actuators such as motors and solenoid valves to amplify the control signal power and provide driving force for them. For example, the motor drives the conveyor belt on the automated assembly line, which is realized by the power amplifier amplifying the signal. At the same time, the characteristics of the power amplifier ensure the high-speed, high-precision and stable operation of the production line, improve production efficiency and product quality, and reduce costs and labor intensity.

Future Outlook: A New Journey for Power Amplifiers
With the development of science and technology, power amplifiers have a broader development space. New materials bring opportunities for them. New semiconductor materials such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) have significant advantages and are emerging in the field of power amplifiers. Gallium nitride power amplifiers are small in size and high in power density. They have great potential in 5G communication base stations, satellite communications and other fields, and are expected to improve signal transmission efficiency and coverage. The integration of digital technology and power amplifiers has become an important trend. Digital signal processing technology can improve the linearity and efficiency of power amplifiers and meet the signal quality requirements of communication systems. In the future, the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning technology is expected to enable power amplifiers to achieve intelligent control, automatically adjust parameters according to the working environment and signal requirements, and improve the quality and efficiency of signal amplification.
Conclusion: Infinite possibilities of signal amplification
As a key device in the field of signal processing, power amplifiers have successfully amplified a variety of signals such as audio, radio frequency, and sensors with their unique working principles and diverse types. They are widely used in many fields such as home audio, mobile phone communications, and industrial automation. It not only brings us immersive music enjoyment and realizes convenient wireless communication, but also ensures the precise control of industrial production, playing an indispensable and key role in modern technology and daily life.
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, the future of power amplifiers is full of infinite possibilities. We have reason to expect that, driven by new materials and new technologies, power amplifiers will continue to break through performance limits, open up a broader world for the development of signal amplification technology, and make greater contributions to the progress of human society.